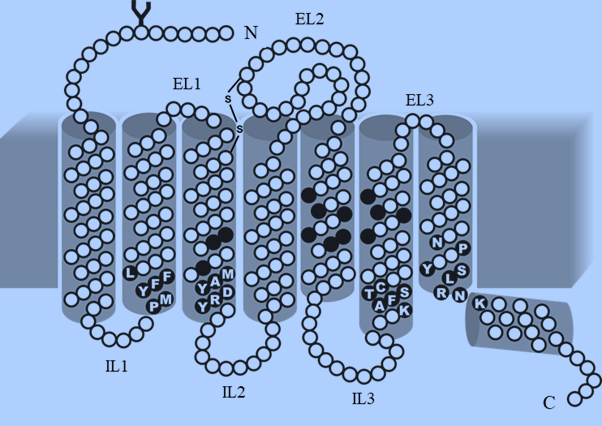
Olfactory Receptors (ORs) are the physical barriers between the environment and the brain.
ORs are members of the GPCR-rhodopsin family, which is involved in cell recognition,
signal transduction activation, and sense mediation. OR is made up of seven transmembrane
(TM) helical domains bound by three putative extracellular loops (EL) and three putative
intracellular loops (IL), an extracellular N-terminus, and an intracellular C-terminus. At the
intersection of TM3 and IL2, the intracellular loop includes a conserved sequence motif, the
aspartate-arginine-tyrosine (DRY) amino acid motif, which is a hallmark of GPCRs. The
TM1, TM2, and TM7 are all conserved. The binding site specificity is determined by the
amino acid side chains of the central TM domains, which are structurally diverse. The
binding pocket of ORs has a hydrophobic environment, indicative of hydrophobic
interactions between odorants and ORs. The binding specificity of ORs is influenced not only
by the central TM-domains hyper-variable region, but also by the N-termini and C-termini.
Both terminals are small, with only about 20 amino acids each. The conserved cysteine
residues in the EL1 and EL2-loops are involved in inter- and intramolecular disulphide
linkages. One of the three cysteine restudies in EL2-loop has a specific role. A metal binding
site is formed by the sequence motif (HXXC[DE]) in EL2-loop. On binding with Zn(II) or
Cu, the EL2-loop transforms into a -helical structure confirmation (eighth helix) (II).When an
odorant with a high affinity for metal ions replaces one of the metal-ligated amino acids in
the EL2-loop, ORs undergo structural rearrangement, which is necessary for the activation of
G-olf proteins attached to OR receptors. On the cytoplasmic side of the TM domains, the
sequence motifs KAFSTC, PMYFFL, and YRDYAM play a role in OR folding and
activation. The amino acid residues on the extracellular side of TM domains are variable,
indicating a wide range of possible odorant recognition sites.
OlfactionBase lists 2067 ORs from two species (Human (851) and Mus musculus (1216)).